How can hydraulic leaks in civil engineering projects be best avoided?
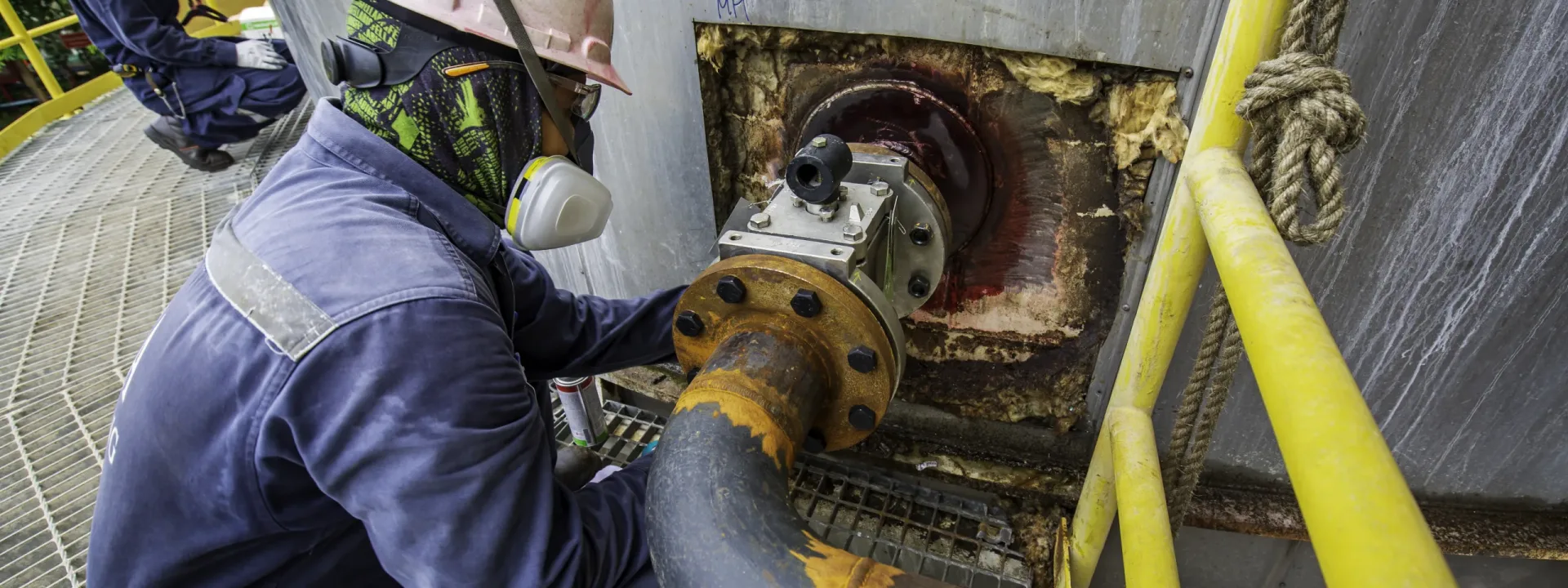
Preventing hydraulic leaks is a critical concern within civil engineering, particularly in projects related to water supply, irrigation, drainage, and flood control systems. Such leaks can lead to extensive environmental damage, structural failures, operational inefficiencies, and safety risks. Thus, it is imperative to proactively mitigate and identify hydraulic leaks through effective strategies and technologies. In this discussion, we will delve into some highly effective methods for preventing hydraulic leaks in civil engineering projects, grounded in principles of hydraulic risk and reliability.
Designing for Reliability
An essential approach to averting hydraulic leaks is to engineer the hydraulic system for reliability. This entails ensuring that the system can effectively perform its intended functions under various circumstances. Key factors include the judicious selection of materials, components, and configurations. Employing safety margins, redundancy, and diversity measures is also critical. For instance, one can opt for corrosion-resistant pipes, valves, and fittings, or incorporate backup pumps, sensors, and controllers. Additionally, utilizing diverse hydraulic components such as flexible hoses, rigid pipes, and hydraulic cylinders tailored to specific applications and environments enhances system resilience.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Another valuable technique for preventing hydraulic leaks involves consistent inspection and maintenance of the hydraulic system. This entails routine assessments of the system’s condition, performance, and operation. It also necessitates prompt repair or replacement of any worn-out or damaged components. Adherence to a meticulously crafted maintenance plan, complete with schedules and procedures, is crucial. The use of appropriate tools, equipment, and techniques is integral to this process. Visual inspection, pressure testing, and leak detection devices are instrumental in identifying and locating any potential leaks. Moreover, the application of cleaning, lubrication, and sealing methods plays a pivotal role in preventing or minimizing leaks.
Remote Monitoring and Control
A third stratagem for preventing hydraulic leaks involves remote monitoring and control of the hydraulic system. This method hinges on employing sensors, meters, and controllers to measure and regulate hydraulic parameters, such as pressure, flow, temperature, and level. To facilitate this, a robust communication network, data acquisition system, and control framework are put in place, complemented by the use of sophisticated software, algorithms, and protocols. Wireless sensors, smart meters, and IoT devices can be deployed to transmit and receive data from the system. The use of systems like SCADA, PLC, or DCS further enables the processing and control of this data, ensuring proactive management of the hydraulic system’s integrity.
Continuous Simulation and Optimization
Another invaluable approach to preempt hydraulic leaks involves an ongoing process of simulating and optimizing the hydraulic system. This means leveraging mathematical models, numerical methods, and computer software to delve into and enhance the hydraulic behavior, performance, and efficiency of the system. This approach relies on the use of data, equations, and criteria, while also tapping into simulation, optimization, and artificial intelligence techniques. To illustrate, one can employ finite element analysis, computational fluid dynamics, or specialized hydraulic simulation software to meticulously model and simulate the system. Additionally, the application of genetic algorithms, neural networks, or machine learning methods facilitates the optimization of the system’s performance, ensuring its continuous refinement.
Constant Training and Education
A fifth critical avenue for preventing hydraulic leaks lies in the consistent training and education of hydraulic system operators, managers, and engineers. This involves equipping them with the essential knowledge, skills, and competencies necessary for the effective and safe operation, management, and design of hydraulic systems. It encompasses the formulation of structured learning objectives, materials, and methodologies, supported by comprehensive training, educational, or certification programs. For instance, the dissemination of manuals, guides, or instructional videos serves to familiarize them with fundamental hydraulic principles, components, and functions. Furthermore, courses, workshops, or seminars keep them abreast of the latest hydraulic technologies, methods, and standards, enabling them to adapt and excel in their roles.
Implementation of Best Practices
A final, fundamental strategy for averting hydraulic leaks involves the rigorous implementation and adherence to best practices pertaining to hydraulic system design, installation, operation, and maintenance. This approach centers around the adoption of established and recommended guidelines, rules, and procedures designed to optimize the hydraulic system’s integrity. Complying with recognized standards, codes, and regulations is instrumental, with periodic audits, reviews, and evaluations reinforcing system reliability. To elucidate, standards such as ISO, ASME, or ANSI can be applied to guide the design and installation of the hydraulic system. Concurrently, regulations from entities like OSHA, EPA, or FEMA provide a framework for the safe and effective operation and maintenance of the hydraulic system.